RestoreGrub2
- Relevant to All editions of PCLinuxOS.
Introduction
Your bootloader may end up corrupt or overwritten by another operating system due to many factors such as user error, power loss or malware etc. In such situations you may find yourself in search of a way to restore your bootloader to a state in which it will normally load your favourite PCLinuxOS.
To fix or restore the GRUB2 bootloader on your PCLinuxOS system you will need to boot a recent PCLinuxOS LiveOS then you can choose one of the 2 methods below depending on whether you prefer using the command-line or graphical user interface.
Using redo-bootloader graphical tool
You will find the redo-bootloader application in the Configuration section of the main menu. If it is missing then install the redo-bootloader package using the Synaptic package manager.
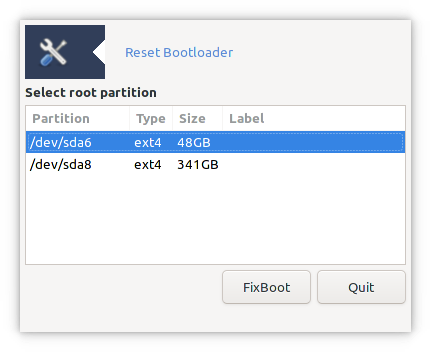
The window shows the Linux partitions available on your system. Select the correct root partition and then click FixBoot. The tool will then mount that partition and enable you to re-install the bootloader.
The first screen allows you to choose where you want to install the bootloader and configure a delay before the system automatically boots.
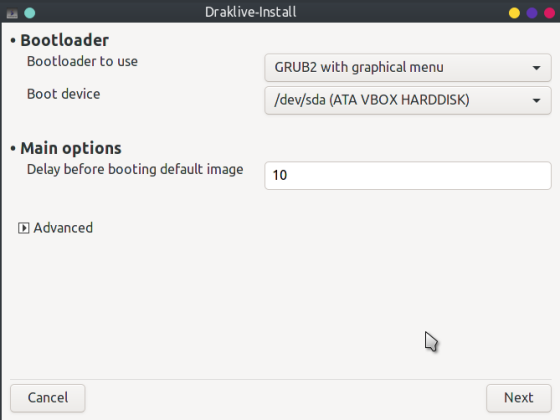
If this is your only Linux install you can select to install to the Master Boot Record (MBR) or EFI System Partition (ESP) depending on whether your system has older BIOS firmware or the newer UEFI firmware. The Master Boot Record (MBR) will always be identified without a partition number such as /dev/sda, /dev/mmcblk0 or /dev/nvme0n1 Usually the default shown in the Boot Device field will be the correct selection.
If you already have previous Linux installs on other partitions you may wish to prevent PCLinuxOS taking over control of the boot from another distro. In the past this would have been achieved by installing the loader to a partition instead of the MBR and then chainloading from the controlling distro. Since GRUB2 does not support installing to a partition you should instead select "Do not touch ESP or MBR" which can be found in the advanced options of the following screen after clicking Next.
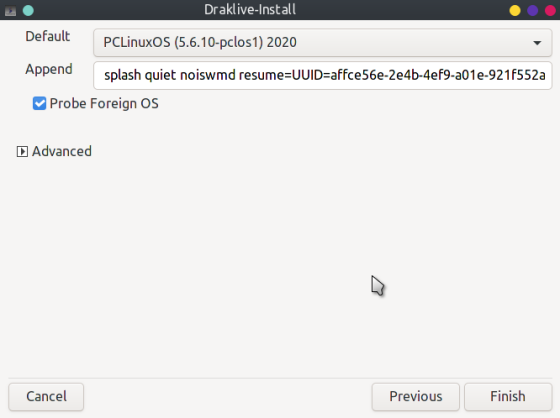
The Probe Foreign OS tick box will allow GRUB to probe for other (non-Linux) OSs and add them to the boot menu.
Click Finish and the bootloader will be (re)installed. Once that is done you should be able to reboot into the installed system.
Using command-line interface
If you prefer to use the command line then open a root terminal and enter the following commands:
mkdir -p /mnt
mount /dev/sdaX /mnt
(replace sdaX with whatever your root partition is)
If this is a UEFI system mount the EFI System Partition (ignore this step for a BIOS/legacy system)
mount /dev/sdaY /mnt/boot/EFI
(replace sdaY with whatever your ESP is)
Run the following commands to re-install the grub bootloader code
for i in /sys /proc /dev; do mount -B $i /mnt$i; done
chroot /mnt
/boot/grub2/install.sh
If all goes well you will see:
Installation finished. No error reported.
Exit the chroot environment with CTRL-D
Undo the mounts and then reboot.
for i in /sys /proc /dev; do umount /mnt$i; done
umount /mnt/boot/EFI #if necessary
umount /mnt
reboot